This is a comprehensive overview of common tablet defects as well as information on effective remedies.
Tablet quality and efficacy are essential factors in pharmaceutical manufacturing. For high standards to be confirmed, it is important to understand the causes and remedies of all the problems that may arise during the production process.
Table of Contents
1. Picking
Definition
The common tablet defects picking are refers to part of the tablet material sticks to the punch face.

Causes
• Excessive moisture or hygroscopic materials.
• Inadequate lubrication.
• Poor quality granules with improper size distribution.
• Over-compression of tablets.
Remedies
• Use a different kind of binder or use less of the current one.
• Alter granulation and compress in a humidity-controlled environment.
• Adjust the mixing procedure.
• Improve the granulation technique and binder quantity.
2. Sticking
Definition
The term “sticking” refers to the tablet material sticks to the die wall or punch surfaces.
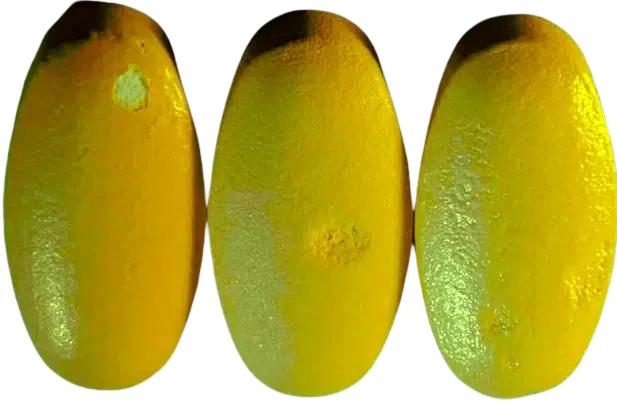

Causes
• Certain formulations contain sticky or hygroscopic components; the tablet substance and the compression tooling are not adequately lubricated.
• The surface finishes of the dies and punches are harsh.
• Insufficient dwell time leads to insufficient granule consolidation.
• An uneven compression force distribution is caused by misalignment or worn-out tooling.
Remedies
• Choose lubricants that are appropriate for the compression and formulation tools.
• Modify the composition or add appropriate excipients to the formulation to make it better.
• Regularly check, clean, and maintain the equipment.
• Find the best compression force and dwell time.
• Replace damaged tooling or perform routine tool calibration.
3. Capping
Definition
The term “capping” defines the partial or whole removal of a tablet’s top or bottom from its body.
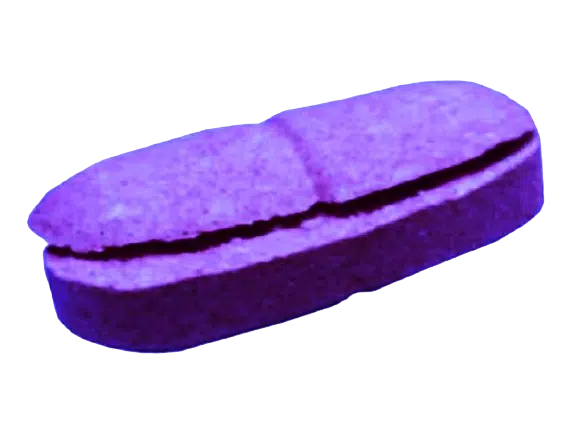

Causes
• Granules containing air that has been captured.
• The granules’ low moisture content.
• High compression speed.
• Insufficient binding agent.
• Inappropriate die filling.
Remedies
• Adjust the granulation process to ensure proper moisture content.
• Slow down the compression speed.
• Use appropriate binding agents and optimize their concentration.
4. Lamination
Definition
Lamination is another common tablet defects and it refers to the separation of a tablet into two or more distinct layers.

Causes
• There is insufficient bonding between the granule layers.
• The cohesive qualities of the granules are diminished by excessive wetness.
• A barrier is formed between the granule layers by air entrapment.
• Inadequate compaction force causes the granule layers to not fully bind.
Remedies
• Provide moisture, binder, and granule size uniformly by using suitable granulation processes.
• Always maintain checking on and regulate the moisture content when granulating.
• Granulation apparatus is used to eliminate air from the granules.
• To maximize compaction and bonding between the granule layers, apply the appropriate compression force.
5. Chipping
Definition
The common tablet defects chipping means breaking or chipping of tablet edges.

Causes
• Too dry or brittle granules.
• Low moisture content.
• High compression force.
• Worn out or damaged punches and dies.
Remedies
• Optimize the moisture content in the granules.
• Use proper lubricants to improve the compressibility of granules.
• Regularly inspect and maintain punches and dies.
• Adjust compression force appropriately.
6. Cracking
Definition
It defines as formation of fine cracks on the tablet surface.
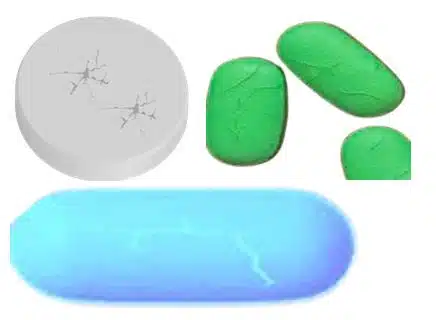
Causes
• Rapid drying of granules.
• Over-compression.
• Use of high tensile strength materials.
Remedies
• Control the drying process to prevent rapid moisture loss.
• Adjust compression force.
• Use materials with appropriate tensile strength.
7. Flashing
Definition
Flashing is another common tablet defects. It is thin, extra material along the tablet’s edges. This is usually the result of compression problems with the process.
Causes
• Overfilling of the die cavity with powder or granules.
• Wear and tear on the punch and die, leading to poor fit and gaps.
• Misalignment of punches and dies during compression
• High compression force causing material to flow out between the punch and die.
• Inappropriate formulation causing poor flow or compression characteristics.
Remedies
• Adjust the powder or granule feed to avoid overfilling the die cavity.
• Use appropriate feed frame settings to ensure consistent die fill.
• Use high-quality tooling materials to reduce wear and for better alignment.
• Adjust the compression force to an optimal level to prevent excess material from being squeezed out.
• Monitor and control compression parameters to maintain consistency.
• To enhance the tablet’s flow and compressibility, improve the mixture.
8. Mottling
Definition
The common tablet defects mottling refers to an uneven distribution of color on the tablet surface, leading to a spotted or blotchy appearance.
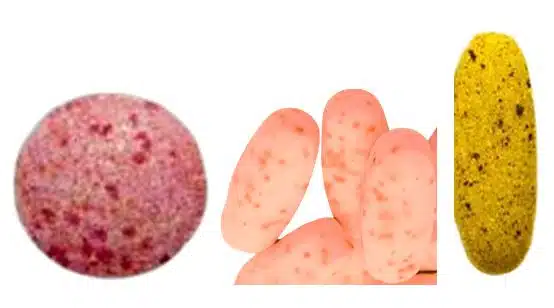
Causes
• Uneven distribution of colorant or dye in the granules.
• Migration of dye during drying.
• Use of insoluble colorants.
Remedies
• Ensure thorough and uniform mixing of colorants.
• Use soluble dyes or colorants.
• Control the drying process to prevent migration of colorants.
9. Binding
Definition
It is also another common tablet defects. The excessive granule adherence to the die surface during compression is referred to as “binding”.
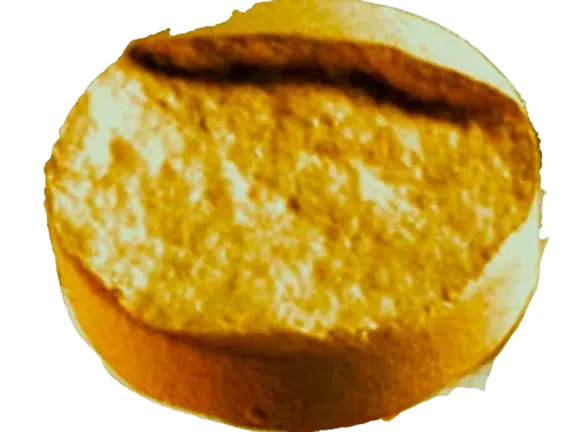

Causes
• Hygroscopic ingredients make the granules sticky and prone to adhesion.
• Another common cause of binding is inadequate lubrication between the dies and the grains.
• High moisture levels can cause the tablet material to stick to the dies.
Remedies
• Lubricate the tablet material and dies appropriately.
• Maintain an eye on and regulate the formulation’s moisture content.
• Develop composition changes to the formulation and include non-hygroscopic excipients.
10. High friability
Definition
Tablets tend to crumble or break easily.

Causes
• Low binder concentration.
• Inadequate compression force.
• Poor granule quality.
Remedies
• Optimize binder concentration.
• Adjust compression force appropriately.
• Improve granule quality through proper granulation techniques.
11. Weight Variation
Definition
Weight variation refers to the significant differences in the weight of tablets. The difference in tablet weight within a batch or between individual tablets is known as weight variation.

The authorized weight variations limit is as follows, under BP and USP:
| BP Specification | USP Specification | Limit |
| Tablet weight 80 mg or less | Tablet weight 130 mg or less | ± 10% |
| More than 80 mg or Less than 250mg | 130 mg to 324 mg | ± 7.5% |
| 250 mg or more | More than 324 mg | ± 5% |
Causes
• Improper granule size distribution.
• Inconsistent die filling.
• Variations in the density of granules.
Remedies
• Ensure uniform granule size distribution through proper sieving.
• Optimize the die filling process.
• Maintain consistent density of granules.
Read Also: DNS IV Infusion Post-Manufacturing Cloudiness Problem
12. Twining
Definition
Twinning refers to the sticking of two or more tablets together, usually occurring during the compression or coating processes.
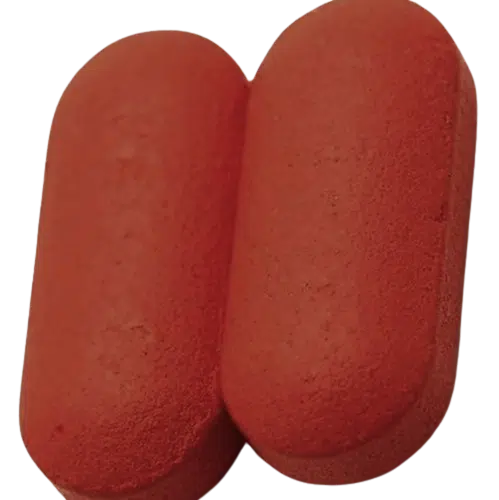

Causes
For Compression:
• Excessive moisture content in granules.
• Inadequate drying of granules or tablets.
• Electrostatic Charges causing tablets to stick.
• Tablets with convex shapes are more prone to twinning.
For Coating:
• High viscosity of the coating solution leading to stickiness.
Remedies
For Compression:
• Ensure proper drying of granules before compression.
• Adjust controlled environments to maintain low humidity.
• Implement grounding and ionizing equipment to control static charges.
• Use flatter tablet shapes or beveled edges to reduce contact points.
• Modify tooling to produce less convex tablets.
For Coating:
• Reduce the viscosity of the coating solution.
• Optimize the spray rate and drying temperature in the coating process.
• Use anti-twinning agents or lubricants in the coating solution.
13. Hardness Variation
Definition
It defines variations in tablet hardness within a batch or between tablets.
Causes
• Inconsistent granule size or moisture content.
• Variations in compression force.
• Uneven distribution of binding agents.
Remedies
• Ensure uniform granulation and moisture content.
• Monitor and adjust compression force regularly.
• Distribute binding agents evenly during granulation.
14. Double Impression
Definition
The common tablet defects double impression is define as the occurrence of two imprints on the tablet.

Causes
• Free rotation of punches during compression.
• Mechanical issues with the press.
Remedies
• Use non-rotating punches.
• Ensure proper maintenance of the tablet press to prevent mechanical issues.
Conclusion
By addressing these defects through careful control of the manufacturing process, pharmaceutical companies can ensure the production of high-quality tablets that meet regulatory standards and provide therapeutic efficacy. Regular monitoring, maintenance, and optimization of the manufacturing processes are essential for achieving this goal.

Abdus Sobhan Salim is professional experienced pharmacist in pharmaceuticals, author and founder of pharmabossbd.com, the first Bangladeshi pharmaceutical blogger since 2019.



