The decision to compile all Quality, Safety, and Efficacy data into a single document, known as the CTD (Common Technical Document), standardized electronic filing transformed the regulatory review processes and made it possible to follow best review practices.
It has been eliminated for companies the need to change the data before sending it to the various ICH regulatory bodies.
Table of Contents
Introduction
The pharmaceutical industry plays a pivotal role in advancing global healthcare by developing, manufacturing, and distributing life-saving medications. This task is achieved through rigorous regulatory processes, one of which is the Common Technical Document (CTD). It serves as a standardized format for submitting regulatory information to health authorities worldwide, streamlining the drug approval process and ensuring consistency and transparency in pharmaceutical documentation. This comprehensive overview delves into the CTD, its structure, purpose, advantages, and significance in the pharmaceutical industry.
Evolution and Purpose of CTD
The development of the Common Technical Document can be traced back to the International Conference on Harmonization (ICH), a collaboration between regulatory authorities and pharmaceutical industry representatives. The primary objective of ICH was to standardize regulatory requirements across regions, promoting the efficient global development and registration of pharmaceutical products.
The CTD, first introduced in 1996, was a groundbreaking initiative by ICH to harmonize the format and content of drug registration dossiers. Its primary purpose is to facilitate the submission of comprehensive and well-organized information about pharmaceutical products to regulatory authorities in a consistent manner. This document streamlines the drug approval process, benefiting both regulators and the pharmaceutical industry.
Structure of the Common Technical Document
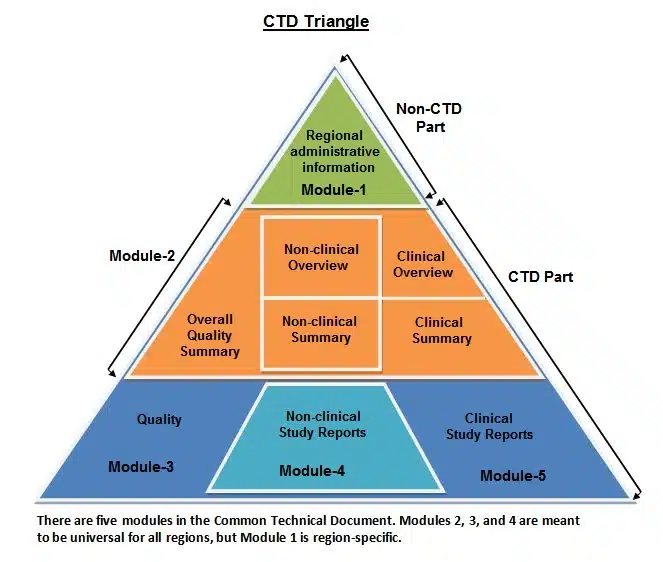
The CTD is structured into five modules, each serving a distinct purpose:
Module 1: Administrative Information
This module contains administrative details such as the cover letter, application form, and regional information.
Module 2: Summaries
Module 2 comprises summaries of the entire dossier, providing an overview of the drug’s quality, safety, and efficacy data. It includes the Quality Overall Summary (QOS), Nonclinical Overview, and Clinical Overview.
Module 3: Quality
The Quality section of the CTD focuses on the chemistry, manufacturing, and controls (CMC) of the pharmaceutical product. It details information about the drug substance, drug product, and the manufacturing process.
Module 4: Nonclinical
Module 4 contains nonclinical data, including studies on the pharmacology, toxicology, and environmental impact of the drug. These studies evaluate the drug’s safety and potential risks.
Module 5: Clinical
The Clinical section of the CTD encompasses all clinical trial data, including study protocols, results, and analyses. It provides a comprehensive overview of the drug’s safety and efficacy in humans.
Advantages of Common Technical Document
The adoption of the CTD format brings several advantages to the pharmaceutical industry and regulatory authorities:
Standardization:
CTD standardizes the format and content of regulatory submissions, reducing the potential for errors and inconsistencies in documentation.
Global Acceptance:
Common Technical Document is widely accepted by regulatory agencies across the world, making it easier for pharmaceutical companies to seek approvals in multiple markets.
Efficiency:
The structured format of Common Technical Documents streamlines the review process for regulatory authorities, leading to faster evaluations and approvals.
Transparency:
It promotes transparency by clearly presenting data on the drug’s quality, safety, and efficacy, enabling regulators to make informed decisions.
Simplified Updates:
When making post-approval changes or renewing licenses, pharmaceutical companies can use the CTD format to submit updated information, ensuring continued compliance.
Significance in Drug Development
The Common Technical Document plays a crucial role in the drug development lifecycle.
Regulatory Submission:
Pharmaceutical companies compile Common Technical Documents as part of their new drug applications (NDAs) or marketing authorization applications (MAAs) and submit them to regulatory authorities for drug approval.
Regulatory Review:
Regulatory agencies, such as the FDA in the United States or the EMA in Europe, review Common Technical Documents to assess the quality, safety, and efficacy of pharmaceutical products.
Post-Approval:
After approval, Common Technical Documents are used for post-marketing surveillance, allowing regulators to monitor the safety and efficacy of drugs in the market.
Global Expansion:
CTD facilitates the expansion of pharmaceutical products into international markets by providing a standardized format that is recognized and accepted globally.
Read Also: FIFO, FEFO, and LIFO Methods in Inventory Control
Challenges and Future Considerations
Despite its many advantages, the use of Common Technical Documents also presents challenges:
Complexity:
Creating a comprehensive CTD can be a complex and resource-intensive process, requiring expertise in various domains.
Updates and Amendments:
Managing post-approval changes and amendments to Common Technical Documents can be challenging, as they must adhere to the same structured format.
Evolving Regulatory Requirements:
Keeping Common Technical Documents compliant with evolving regulatory requirements can be demanding, as these requirements may change over time.
To address these challenges, the pharmaceutical industry and regulatory authorities must collaborate to continuously improve the CTD format and streamline its use.
Conclusion
The Common Technical Document is a cornerstone of the pharmaceutical industry, streamlining the regulatory process and ensuring the safety and efficacy of drugs. Its standardized format and comprehensive structure benefit both pharmaceutical companies and regulatory authorities by promoting transparency, global acceptance, and efficiency in drug development. While challenges exist, the CTD remains an essential tool in advancing healthcare worldwide, making it a vital component of pharmaceutical innovation and patient care.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why was the CTD developed?

The CTD was developed to harmonize the format and content of regulatory submissions worldwide, making it easier for pharmaceutical companies to seek approval in multiple countries.
How does the CTD benefit pharmaceutical companies?
The CTD streamlines the regulatory submission process, reduces duplication of efforts, and facilitates global marketing authorization applications.
What is the role of the Quality module in the CTD?
The quality module provides detailed information about the drug’s manufacturing, chemistry, and controls to ensure product quality and consistency.
What information is included in the Nonclinical module of the CTD?
The Nonclinical module contains data from animal studies and laboratory tests to assess the drug’s safety and pharmacology
What does the Clinical module of the CTD cover?
The Clinical module presents data from human clinical trials, including safety and efficacy results, to support the drug’s approval.

Abdus Sobhan Salim is professional experienced pharmacist in pharmaceuticals, author and founder of pharmabossbd.com, the first Bangladeshi pharmaceutical blogger since 2019.




This is best information for pharma
Professionals
Thanks
Hi there
Just checked your pharmabossbd.com baclink profile, I noticed a moderate percentage of toxic links pointing to your website
We will investigate each link for its toxicity and perform a professional clean up for you free of charge.
Start recovering your ranks today:
https://www.hilkom-digital.de/professional-linksprofile-clean-up-service/
Regards
Mike Baker
Hilkom Digital SEO Experts
https://www.hilkom-digital.de/