A Stability Study Protocol outlines procedures to assess a product’s shelf life under various conditions, ensuring its quality, safety, and efficacy over time through systematic testing and analysis.
1. DEFINITION
This proposal was developed within the context of the International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) guidelines. The guideline provides general instruction on the requirement of stability testing and encompass the practical flexibility required for specific scientific situations and characteristic of the products being evaluated.
2. PURPOSE
To determine the shelf life of the product and to ensure the stable formulation throughout the specified shelf life of the product.
3. SCOPE
Stability testing is carried out to give evidence of how a drug’s or product’s quality changes over time under the effect of different environmental factors, such as:
-Temperature
-Humidity
The enable recommended storage conditions retest periods and shelf life of the product under considerations.
4. DRUG PRODUCT
Formulation feasibility study:
Objective:
Initial objective is to provide data to enable optimized formulation is to be chosen.
5. ROUTINE STABILITY STUDIES
This involves stability studies on already marketed products based on time-to-time analysis
of the retention sample and stability sample. The first three batches of a marketed product
maintained this protocol.
Objectives:
To generate real time data on the marketed products in order to confirm and extended (if required) the shelf life predicted from earlier studies.
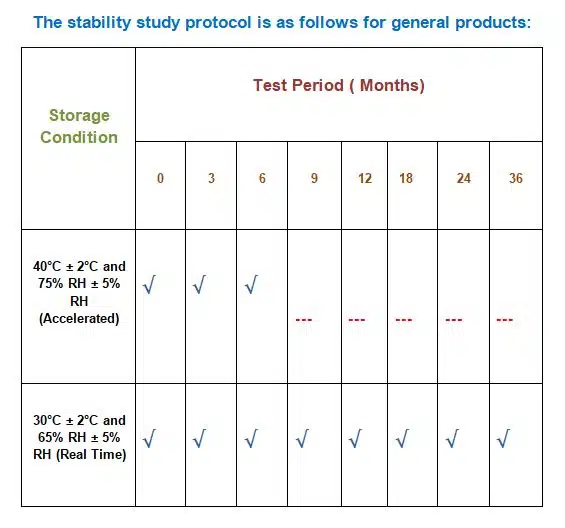
The stability study protocol is as follows for general products:
| Storage Condition | Test Period ( Months) | |||||||
| 0 | 3 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 36 | |
| 40°C ± 2°C and 75% RH ± 5% RH (Accelerated) | √ | √ | √ | – | – | – | – | |
| 30°C ± 2°C and 65% RH ± 5% RH (Real Time) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
√ = Examine for physical and chemical test
Significant changes which indicates instability refers to:
A deviation of 5% or more from the initial result of the assay or a failure to reach the potency approval criteria.
Any specified degradation product exceeding it’s acceptance criteria.
Failure to meet the acceptance criteria for the product’s dissolution.
Failure to meet the acceptance criteria for the product’s appearance, physical properties, e.g color, hardness, disintegration time etc.
Read Also: Product Management Department in The Pharmaceutical Industry (PMD)
Sampling requirement
Sample size (for a single batch/storage state)
Accelerated Stability Study
– Appearance: 0* tablets number of testing: 2 times
– Water content : 8 tablets Quantity needed
– Disintegration: 6 tablets = 2 x 6 tablets
– Dissolution: 6 tablets = 2 x 6 tablets
– Content & impurity: 10 tablets = 2 x 20 tablets
Total = 2 x 40 tablets
Note: This observation was made from certain tablets kept for other tests
Real Time Stability Study
– Appearance : 0* tablets number of testing : 7 times
– water content : 8 tablets quantity needed
– disintegration : 6 tablets = 7 x 6 tablets
– dissolution : 6 tablets = 7 x 6 tablets
– content & impurity : 10 tablets = 7 x 20 tablet
Total = 7 x 20 tablets
Note: This observation was made from certain tablets kept for other tests
Documentation:
For future reference, all manufacturing, analytical, and other document data must be collected within a project file which is easily available.
People Also Read:
Supply Chain Management (SCM) in the Pharmaceuticals
FIFO, FEFO, and LIFO Methods in Inventory Control
Common Technical Document (CTD) Modules

Abdus Sobhan Salim is professional experienced pharmacist in pharmaceuticals, author and founder of pharmabossbd.com, the first Bangladeshi pharmaceutical blogger since 2019.



