In pharmaceutical industry tablet manufacturing process is a complex method that involves several stages blending, granulation, compression, Coating and packaging to ensure that the final product is of high quality, meets regulatory standards, and is effective.
Tablet is a solid dosage form of medication, where the active ingredient is combined with various excipients and compressed into a small, flat, or round shape for oral consumption. Tablets are one of the most common forms of medication delivery due to their convenience, stability, and ease of mass production. They can be formulated for immediate release, delayed release, or extended release, depending on the therapeutic need. Tablets often include coatings to mask unpleasant tastes or to protect the active ingredient from stomach acid, enhancing patient compliance and drug efficacy.
Table of Contents
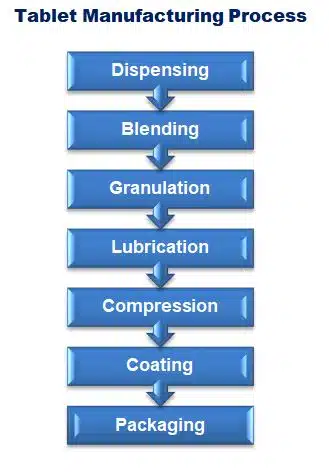
Now we relate the key stages of tablet manufacturing:
Dispensing for Tablet Manufacturing
At first select the right ingredients (active pharmaceutical ingredients or APIs and excipients) and their proportions as per Batch Manufacturing Record (BMR)
The dispensing stage in tablet manufacturing is the initial phase, where raw materials, including active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and excipients, are accurately weighed and measured. This stage ensures that each component is dispensed according to the precise quantity required by the formulation. Proper dispensing is essential for maintaining uniformity and consistency in the final product. Any error at this stage can lead to batch failures or inconsistencies in tablet potency and quality. The process involves strict adherence to standard operating procedures (SOPs), with thorough cross-checking and documentation to ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
Blending (Mixing) for Tablet Manufacturing
The blending stage in tablet manufacturing is a critical process that ensures uniform distribution of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and excipients within a batch. During this stage first all powders materials should sheave before added to mix into blender. Blending is important to achieve homogeneity, which is essential for consistent drug dosage and efficacy.
The blending process typically involves the use of equipment like V-blenders, ribbon blenders, or high-shear mixers, depending on the properties of the materials. Proper blending helps in preventing issues like segregation, poor flow ability, and tablet weight variation, which can impact the overall quality of the final product. Attention to factors such as blending time, speed, and material compatibility is crucial to avoid over-blending, which can lead to material degradation or under-blending, resulting in dose inconsistencies.
Granulation for Tablet Manufacturing
This stage is improve the flow ability and compressibility of powders to ensure consistent tablet production.
Granulation is a key process in tablet manufacturing that involves forming larger, multi-particle entities from fine powders to improve their flow ability, compressibility, and content uniformity. The process enhances the physical properties of the raw materials, making them easier to handle and suitable for further processing like tableting.
Granulation can be achieved through two primary methods: wet granulation, where a liquid binder is added to form granules, and dry granulation, which compresses powders directly without the use of a liquid. The choice of method depends on the characteristics of the drug and excipients, as well as the desired tablet properties.
Types of Granulation:
Wet Granulation: A liquid binder is added to the powder blend, and the wet mass is granulated. Afterward, it’s dried and milled.
Dry Granulation: No liquid binder is used. The powder mixture is compressed into slugs or compacted, followed by milling to produce granules.
Direct Compression: Some APIs and excipients are sufficiently compressible, eliminating the need for granulation.
Drying for Tablet Manufacturing
The drying stage in tablet manufacturing is a critical step that occurs after the granulation process, where the wet granules need to be dried to achieve the desired moisture content. This process is essential for ensuring proper tablet hardness, preventing degradation, and maintaining product stability. The most common drying methods include tray drying, fluid bed drying, and vacuum drying.
In fluid bed dryer, hot air is passed through the granules to evaporate moisture uniformly. In tray drying, granules are spread out on trays and exposed to heated air, while vacuum drying uses reduced pressure to remove moisture at lower temperatures. Proper control of drying parameters is crucial to avoid over-drying, which can lead to brittle granules, or under-drying, which can result in moisture retention and poor tablet integrity.
Lubrication for Tablet Manufacturing
Lubrication in tablet manufacturing is a critical stage that ensures proper compression and ejection of tablets without sticking or causing friction. It typically occurs after the granulation and before the compression stages. This stage is important to prevent sticking of granules to the tablet punches, reduce friction between the tablets and die wall, and ensure smooth ejection during compression. The lubricant is blended with the granules or powder mix in a blender for a short period to avoid over-mixing, which could affect tablet hardness and disintegration time.
Examples: Common lubricants include magnesium stearate, stearic acid, talc, or polyethylene glycol (PEG). Magnesium stearate is one of the most widely used lubricants.
Compression for Tablet Manufacturing
In this stage compress the granules or powder mixture into tablets. The compression stage in tablet manufacturing is an important step where the powdered formulation is transformed into a solid, compact tablet. It involves several key processes:
At first, the powder blend is fed into a die cavity, where a punch applies pressure to compact the powder into a tablet shape.
This compression process is typically performed using a rotary tablet press, which consists of upper and lower punches that move in and out of the die, compressing the powder into the desired thickness and hardness.
The pressure applied must be optimized to ensure proper tablet hardness, uniformity, and durability without causing excessive wear on the tooling or degradation of the active ingredients.
After compression, the tablets are ejected from the machine and are subjected to quality control checks to ensure they meet the required standards for weight, hardness, and disintegration. This stage is essential in ensuring that the tablets will perform effectively when used by patients or consumers.
Coating for Tablet Manufacturing
The coating stages of the tablet manufacturing process involve several key steps to ensure a uniform and protective layer is applied to the tablet core. First, the tablets are loaded into a coating pan or drum where they are rotated to ensure even exposure. A coating solution, which may consist of polymers, plasticizers, colorants, and other excipients, is sprayed onto the tablets. As the solution is applied, warm air is circulated to evaporate the solvent, allowing the coating to adhere and form a smooth film. Multiple layers may be applied depending on the desired thickness and function of the coating, such as protection, taste masking, or controlled drug release.
Types of Coating:
Sugar Coating: A traditional method that involves applying layers of sugar.
Film Coating: A polymer-based coating that forms a thin film around the tablet.
Enteric Coating: A coating that prevents the tablet from dissolving in the stomach, allowing it to pass into the intestine for absorption.
Quality Control (QC) Testing
Quality Control (QC) testing is an essential part of the tablet manufacturing process to ensure that the final product meets the required standards of quality, safety, and efficacy. QC testing occurs at various stages, including raw material testing, in-process control, and finished product evaluation. First, the active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and excipients undergo rigorous testing to ensure their purity, identity, and potency.
During the manufacturing process, in-process tests are conducted to monitor parameters like weight variation, hardness, thickness, friability, and disintegration time of the tablets. These tests help in identifying any deviations from the specified formulation or process standards. Finally, the finished tablets are subjected to more comprehensive testing, including dissolution testing to assess the drug release profile, assay testing to verify the active ingredient content, and microbiological tests to ensure that there are no toxic components in the product.
Each of these QC stages is important to maintaining the consistency, efficacy, and safety of the tablet before it reaches the market.
Tests Conducted:
Hardness Testing: Determines the mechanical strength of the tablet.
Friability Testing: Measures how easily a tablet breaks or crumbles.
Weight Variation: Ensures consistent tablet weight.
Content Uniformity: Ensures each tablet contains the same amount of API.
Disintegration Test: Determines the time it takes for a tablet to break down in a solution.
Dissolution Testing: Checks how quickly the tablet dissolves and releases the API.
Assay: Ensure the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in the tablet is quantified to ensure its concentration matches the label claim, confirming the dosage’s accuracy
Packaging
The packaging stages of tablet manufacturing play a crucial role in ensuring the safety, stability, and proper distribution of the product. The process begins with primary packaging, where tablets are placed in direct contact with protective materials such as blister packs, bottles, or foil strips. This step is designed to shield the tablets from environmental factors like moisture, air, and contamination.
Next is secondary packaging, which groups the primary packages into larger units, often in boxes or cartons, providing additional protection and aiding in labeling, branding, and instructions for use.
Finally, in the tertiary packaging stage, multiple secondary packages are packed for bulk transport and storage, using crates, pallets, or shrink wraps, ensuring the safe distribution of the product from the manufacturing site to the final point of sale or use. Each stage is vital for maintaining the quality and efficacy of the tablets throughout their shelf life.
Storage and Distribution
The storage and distribution stages of the tablet manufacturing process are crucial to maintaining product integrity and ensuring safe delivery to end users. After the tablets are produced, they are stored in controlled environments to prevent degradation. This includes protecting them from moisture, light, heat, and contamination. Proper labeling, batch tracking, and adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) ensure the products remain traceable and safe. The distribution process involves packaging the tablets securely, often in blister packs or bottles, and shipping them to wholesalers, pharmacies, or retailers. Careful consideration is given to transportation conditions, particularly temperature control, to ensure the tablets maintain their potency and effectiveness throughout their shelf life.
Regulatory compliance and quality control checks at each stage ensure the product reaches consumers safely and in optimal condition.
The tablet manufacturing process involves several critical steps to ensure the production of high-quality, uniform tablets. These steps include blending, granulation, compression, and coating, each designed to ensure the proper dosage, stability, and release profile of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API). The process ends with rigorous quality control checks to meet industry standards for safety, efficacy, and consistency before the tablets are packaged for distribution.
Related Topics:
- DNS IV Infusion Post-Manufacturing Cloudiness Problem
- Role of PPIC in Pharmaceuticals (Production Planning & Inventory Control)
- Common Tablet Defects and Remedies in Manufacturing
- Difference Between Drugs and Medicines
- Cefixime Trihydrate PFS Formulation and Manufacturing Process 2024
- Azithromycin PFS Formulation and Manufacturing Process

Abdus Sobhan Salim is professional experienced pharmacist in pharmaceuticals, author and founder of pharmabossbd.com, the first Bangladeshi pharmaceutical blogger since 2019.